

Biometric Authentication is an identity verification process that uses an individual’s unique characteristics, such as fingerprint, face, voice, or iris. This technology has become very popular due to its high level of security and difficulty of counterfeiting compared to traditional methods such as passwords and secret codes.
Fingerprints: One of the oldest and most widely used biometric authentication methods. Based on the unique fingerprint pattern, it is fast and easy to use.
Facial recognition: This type of authentication uses a person’s unique facial patterns and features. This technology is constantly being developed to improve its accuracy and reduce the possibility of error.
Iris recognition: This method uses the unique iris patterns in individuals’ eyes. It is considered one of the safest methods due to the complexity of the patterns and the difficulty of imitating them.
Voice recognition: This method analyzes individuals’ unique voice characteristics, such as tone and speech pattern. This technology is useful in environments that require hands-free or in voice control use cases.
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the appropriate method depends on the security requirements and context in which it will be used. Technology continues to evolve to improve the accuracy and security of these systems, making them an integral part of many security systems in the modern world.
Implementing Biometric Authentication in mobile applications offers several important benefits:
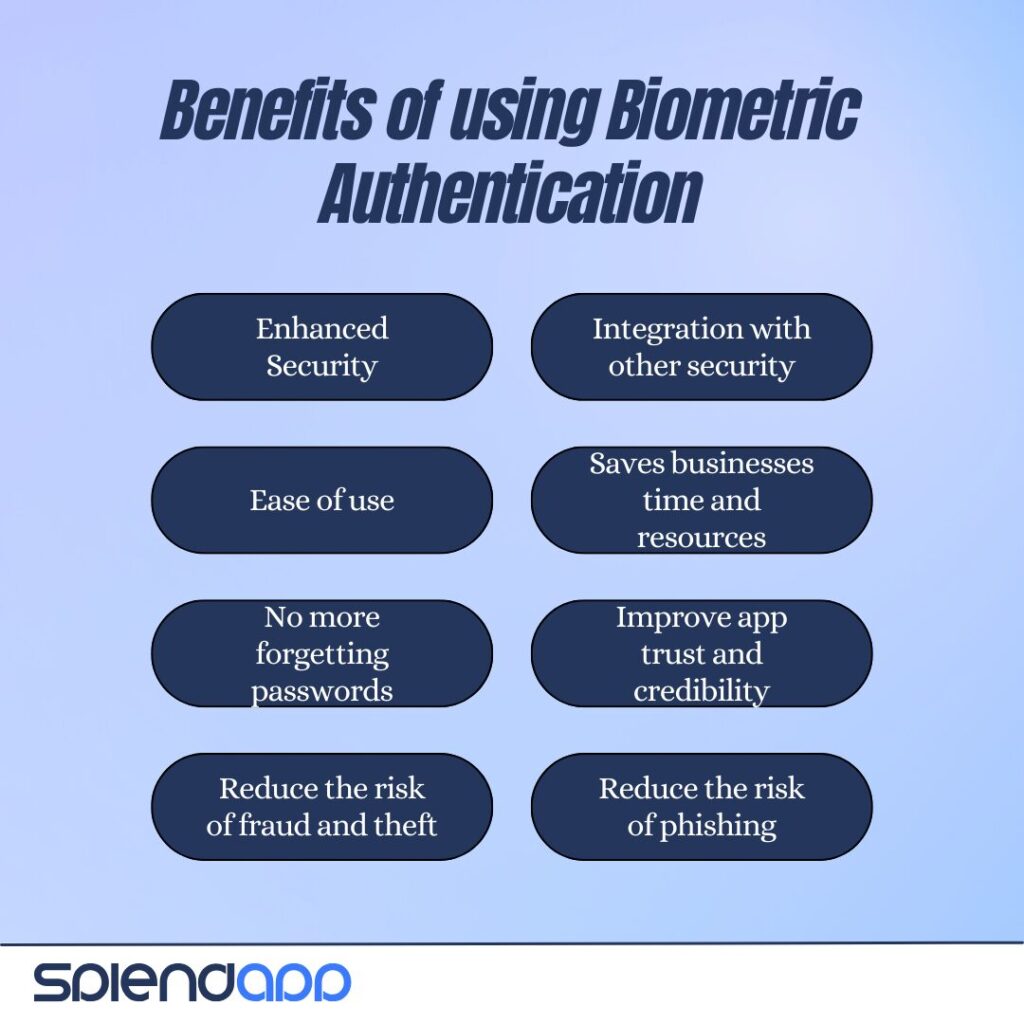
Enhanced Security: Biometric Authentication provides a much higher level of security compared to traditional passwords. Since biometric data is unique to each individual, it is very difficult to fake or steal.
Ease of use: Accessing apps using your fingerprint or facial recognition is much faster and easier than typing in a password. This improves the user experience and increases access speed.
No more forgetting passwords: Because biometric authentication uses physiological characteristics, users don’t need to remember multiple passwords, reducing the risk of forgetting them or having to constantly reset them.
Reduce the risk of fraud and theft: With biometric authentication, it becomes more difficult for fraudsters to access personal accounts because they need the user’s actual biometric data.
Integration with other security technologies: Biometric authentication can be integrated with other security technologies, such as encryption and multi-factor security, to provide comprehensive protection.
Saves businesses time and resources: Reduces the need for technical support for password issues and improves the overall efficiency of security systems.
Improve app trust and credibility: Mobile apps that use biometric authentication demonstrate a commitment to security, which enhances users’ trust in them.
Reduce the risk of phishing: Biometric authentication is difficult to fool through phishing techniques that often target passwords.
In short, implementing biometric authentication in mobile applications provides a perfect balance between security and convenience, making it a preferred solution in many scenarios.
Biometric Authentication in mobile applications depends on several basic steps and technical considerations. Here’s the general process and some important tips:
Choose the type of biometric authentication: Decide which type of biometric authentication you want to use (fingerprint, facial recognition, iris recognition, voice recognition, etc.).
Device and requirements analysis: Check the capabilities of the device that will use the application. Some mobile devices may not support all types of biometric authentication.
Use standard APIs: Use application programming interfaces (APIs) available in the operating system to integrate biometric authentication. For example, Android provides BiometricPrompt API, And iOS provides face ID and touch ID.
Implement multi-factor security: To increase security, it is best to combine biometric authentication with other methods such as passwords or secret codes.
Handle biometric data with caution: Ensure that user biometric data is properly protected. This data should not be stored on remote servers and should preferably remain local on the device.
User Interface Design: Design an easy, clear user interface that guides users through the authentication process.
Test and verify performance: Test the application to ensure that biometric authentication works properly in various scenarios and usage conditions.
Handling exceptional cases: Make sure there is an alternative method of authentication in case biometric authentication does not work (such as a password or PIN).
Compliance with laws and regulations: Make sure your app adheres to local and international laws and regulations related to privacy and data protection.
Update and Maintenance: Update the application regularly to ensure the highest levels of security and compatibility with the latest biometric technologies.
By following these steps, you can effectively integrate biometric authentication into your mobile applications to provide an enhanced and convenient security experience for users.
In conclusion, talking about biometric authentication has proven itself as one of the most effective and secure methods of identity verification in our current era. With its advanced technology based on individuals’ unique physiological and behavioral characteristics, biometric authentication provides a high level of security that is difficult to crack, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, from personal devices to large security systems.
However, we must be aware of the challenges related to privacy and data protection, as storing and processing biometric data requires high levels of security and compliance with laws and regulations. The development of these technologies must be carried out with ethical considerations and respect for the privacy of individuals.
In the future, biometric authentication is expected to continue to evolve and become more integrated into our daily lives, whether in banking systems, access control, mobile applications, and other areas. In addition, we are likely to see improvements in the accuracy and ease of use of these technologies, enhancing their broader acceptance and diffusion.